The Allen Institute for Brain Science (Allen Institute) maintains an SDK, called the Allen SDK, for working with their resources (data and services). This notebook, allensdk_on_colab.ipynb, is focused on nothing except the installation of the Allen SDK on Colab.
The following snippets were tested on Colab in new notebooks, for both options available on Colab: Python 2 and Python 3.
Herein, AllenSDK and allensdk refer to the Python package that gets imported, which is distinct from "the Allen SDK" which is AllenSDK plus further documentation, example code, etcetera that can be found in the Allen Instutute's repository.
Motivation
This notebook was built out while working through – on Colab – the Allen Institute's pedagogical Jupyter notebooks in both the Allen SDK and their Summer Workshop on the Dynamic Brain repository on GitHub.
The Allen SDK documentation includes example Jupyter notebooks for how to use AllenSDK.
Separately, the Allen Institute holds an annual two week retreat, the Summer Workshop on the Dynamic Brain (SWDB), where they train up promising new neuroscientist on how to do science with the Allen Institute's data and tools. The main pedagogical medium in AllenSDK and SWDB repos is Jupyter notebooks, which can be found on GitHub, AllenInstitute/AllenSDK and AllenInstitute/SWDB_2018, respectively.
The SWDB notebooks assume that AllenSDK is preinstalled. That is, in order to get an arbitrary, as-found-on-GitHub SWDB notebook to work in Colab, a !pip install allensdk is required first.
On Colab, a single user is provided a single virtual machine (VM) which has a file system. Both the VM and it's file system are transient, with a maximum lifetime of 12 hours (supposedly) but they can get killed off in as little as 60 minutes due to being idle (the only persistant info is the notebook itself, stored on Google Drive not the local file system). But for the lifetime of a given VM, the AllenSDK only need be installed once, after which any notebook can import allensdk.
(Note: in Colab both Python 2 and Python 3 notebooks can be run. Installing allensdk in a Python 2 notebook does not make import allensdk work in a Python 3 notebook on the same Colab VM, and vice versa.)
This file makes it trivial to repeat (and debug) AllenSDK installs as needed – which can be rather frequent on Colab. The pip install is just one line of code; the real value here is this text and the collection of debug tools that can come in handy if set-up does not going well.
Install This File as Colab Custom Snippets
This notebook reads well enough as one sequential story but the text is really designed to read well as individual snippets, in Colab's code snippet insert dialog.
To "install" these snippets in your Colab snippets library:
- Load this file in Colab
- Copy the URL (~
https://colab.research.google.com/...) - In any Colab page, from the menus select
Tools=>Preferences... - In
Custom snippet notebook URL, paste the URL - Press
Save - Reload
Note: Colab does allow for multiple simultaneous Custom snippet notebook URLs... sometimes and sometimes not.
After the above set-up, it's trivial to insert cells that install and test AllenSDK. For example, load in Colab a SWDB notebook, say BrainObservatory.ipynb, then simply select Insert => Code snippet... and search for allensdk and the following come up:
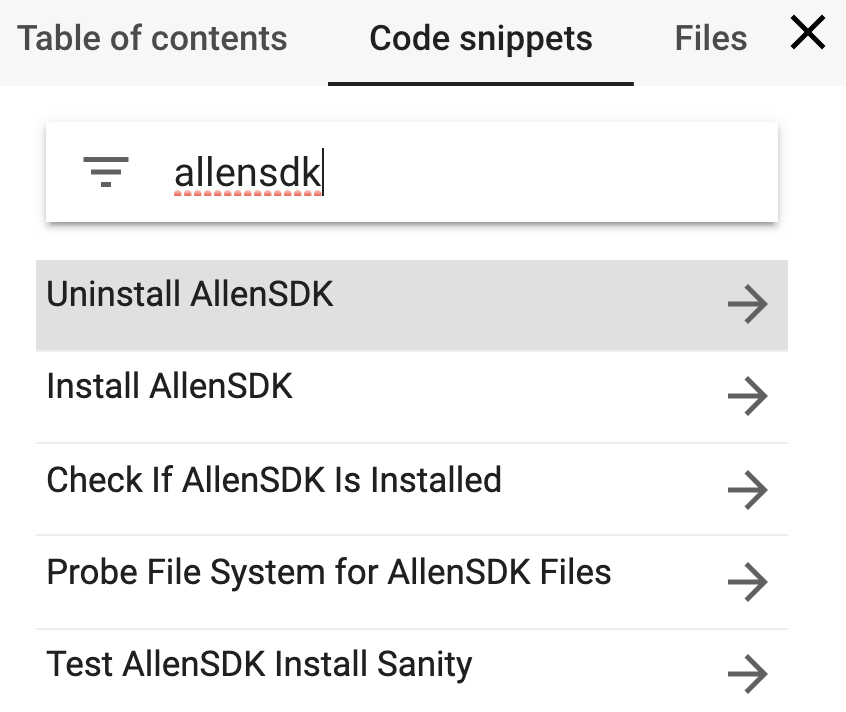
Select Install AllenSDK and run the resulting code cell, after which the Allen notebooks should work on Colab. Your modification will not persist in the GitHub hosted repo's copy of BrainObservatory.ipynb (i.e. the notebook is in playground mode).
Ergo, these snippets provide a relatively easy way to play with the Allen pedogogical notebooks on Colab, short of forking the original repo... which is one of the things Colab is really useful for.
# One liner install of AllenSDK
!pip install allensdk
TODO: maybe only !pip if detect AllenSDK not installed.
# One liner uninstall of AllenSDK, --yes only works with pip >= 7.1.2
!pip uninstall --yes allensdk
Note that if AllenSDK is not installed then pip uninstall -yes allensdk will return: "Skipping allensdk as it is not installed" as expected.
The --yes option works with pip version 7.1.2 and above, and is used here to avoid things hanging at a confirmation dialog (A "Do ya really wanna uninstall all these dependencies?" sort of thing.)
Note that the following sort of sequence can be confusing:
- Install
AllenSDK(pip install allensdk) - Instantiate some class, say,
allensdk.api.queries.rma_api - Uninstall
AllenSDK(pip uninstall allensdk) - Instantiate again
allensdk.api.queries.rma_api
It may come as a surprise that step #4 does not throw a ModuleNotFoundError. Point is AllenSDK was uninstalled but the Python runtime still had classes already parsed into the runtime. Those classes will persist until a runtime restart. So, if you really want to uninstall AllenSDK you might want to consider a runtime restart to really flush out the system. (This issue is true of Python in general; it is not an AllenSDK thing.)
TODO: confirm the above again, with some more testing.
TODO: Maybe importlib can improve this via, say, invalidate_cache().
# Python2: Check If AllenSDK Is Installed
# via https://stackoverflow.com/a/14050282
import imp
import pkg_resources
try:
imp.find_module('allensdk')
found = True
except ImportError:
found = False
if found is True:
import allensdk
vers = allensdk.__version__
message = "AllenSDK is installed. Version: " + vers
print(message)
else:
print("AllenSDK is NOT installed")
# Python3: Check If AllenSDK Is Installed
import importlib.util
import pkg_resources
import sys
# See https://stackoverflow.com/a/41815890
package_name = "allensdk"
spec = importlib.util.find_spec(package_name)
if spec is None:
print(package_name +" is NOT installed")
else:
print("%s (version: %s) is installed." % (package_name, pkg_resources.get_distribution("allensdk").version))
Note that this can return a false result if AllenSDK classes were instantiated followed by a pip uninstall allensdk. In that case this test will still report that allensdk is installed, until the runtime is restarted.
Note, if this Python3 code is run inside Python2 notebook, then the result will be ImportError: No module named util.
TODO: Guess this should be enhanced to first check if the user is using the appropriate test version (python2 vs python3). Or maybe even combine both tests into one. That sounds more elegant and foolproof.
Probe File System for AllenSDK Files
From the output of the above pip install is seems packages are getting installed in /usr/local/lib/python3.6/dist-packages (or similar for python2) so might be interesting to see what allensdk related stuff shows up after a pip install allensdk. Two items usually show up, allensdk and an allensdk-0.xy.z.dist-info where x,y,z are digit charters corresponding to the version number installed.
# Probe File System for AllenSDK Files
import os
import platform
import site
allensdk_was_found = False
sites = site.getsitepackages()
for a_site_dir_name in sites:
if os.path.isdir(a_site_dir_name):
maybe_allensdk_install_dir = os.path.join(a_site_dir_name, "allensdk")
if os.path.isdir(maybe_allensdk_install_dir):
allensdk_was_found = True
a_message = "AllenSDK looks to be installed in:\n " + maybe_allensdk_install_dir + "\n"
print(a_message)
import allensdk
vers = allensdk.__version__
vers_message = "AllenSDK installed version seems to be:\n " + vers + "\n"
print(vers_message)
dist_info_dir_name = "allensdk-" + vers + ".dist-info"
full_path_dist_info_dir_name = os.path.join(a_site_dir_name, dist_info_dir_name)
another_message = "AllenSDK dist-info directory name:\n " + full_path_dist_info_dir_name + "\n\nContents of dist-info dir:"
print(another_message)
!ls {full_path_dist_info_dir_name}/
if allensdk_was_found == False:
failed_message = "AllenSDK does not appear to be installed for Python " + platform.python_version()[0]
print(failed_message)
This is a trivial sanity checker to confirm that AllenSDK is installed and working within a machine. This can be quite useful on Colab (and the like) where VMs are getting tossed away on a regular, frequent schedule. Just run this cell and if fetched_data is an array with one more elements and there are no errors, one can assume AllenSDK is a happy camper.
If this next cell throws ModuleNotFoundError that is an indication that AllenSDK is not installed.
# Perform a simple test query against the Allen Institute public RESTful API
#
# TODO: Intentionally defeated cache? or complexing issues, are we here?
# Maybe a network test snippet would be good. With random string in the query criteria
from allensdk.api.queries.rma_api import RmaApi
rma = RmaApi()
fetched_data = rma.model_query('Atlas', criteria="[name$il'*Human*']")
if len(fetched_data) > 0:
print( "Length of fetched_data: ", (len(fetched_data)) )
else:
print( "WARNING: Zero data records fetched. Probably a failure." )
